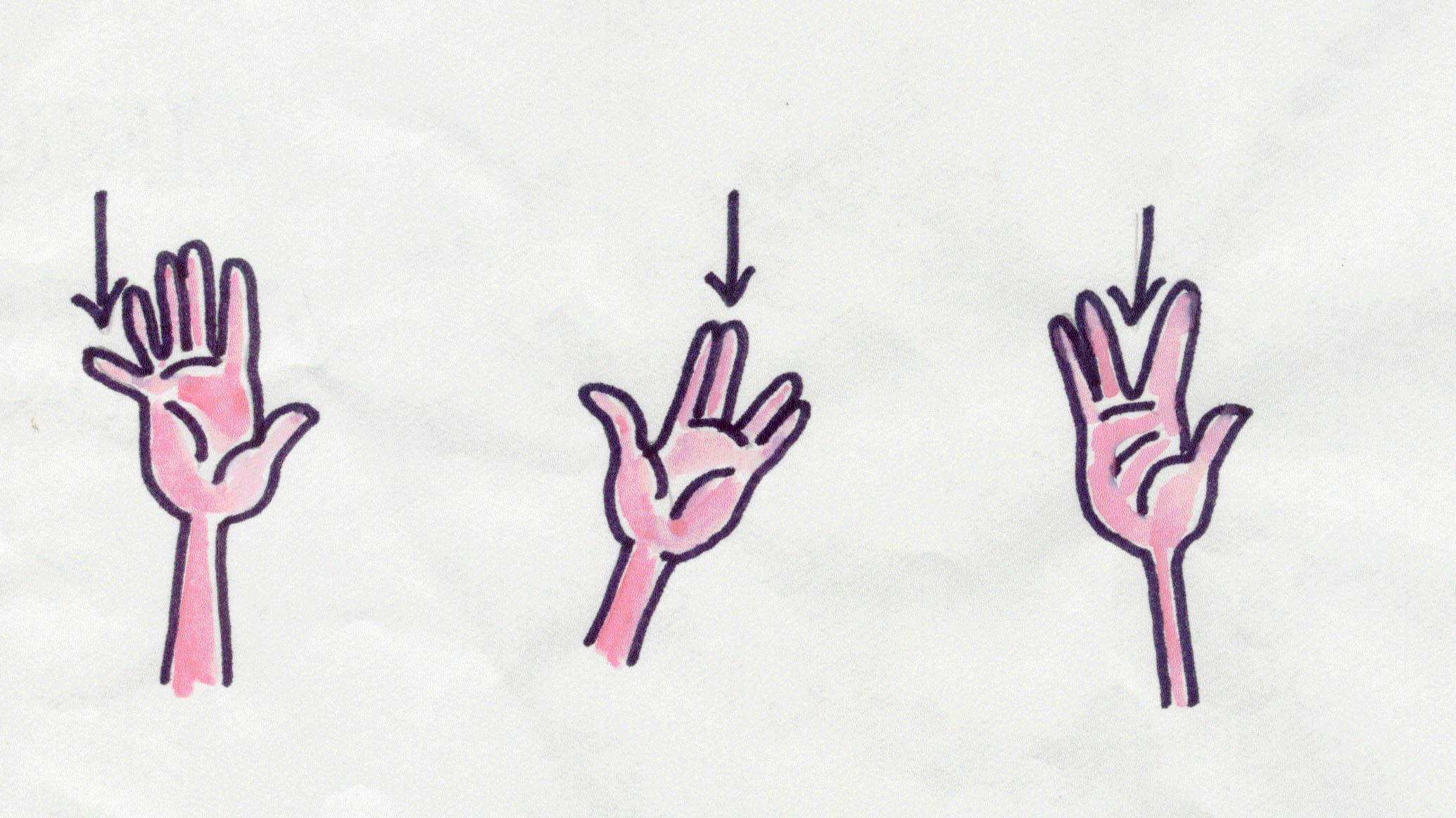
1. Deformity of the hand
What is DEFORMITY?
When any part
of the body is not formed normally, and there is an abnormal feature with
regard to the size or shape of that part, we call that Deformity. This
is a congenital deformity,
since it occurs at birth.
DEFORMITIES
1. Deformity of the
hand 
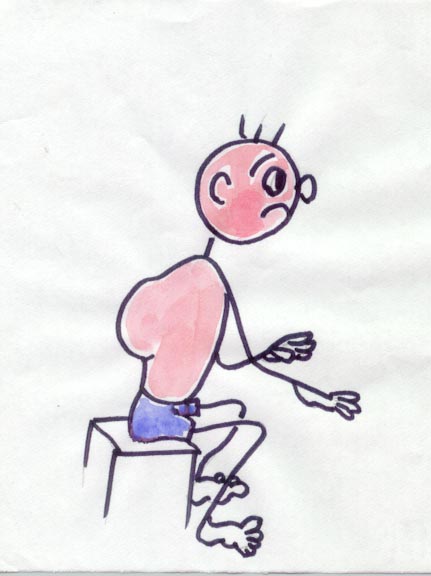 2.
Deformed spine
2.
Deformed spine
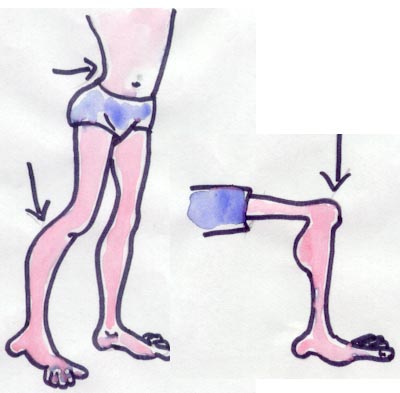 4.
Deformity of the knee
4.
Deformity of the knee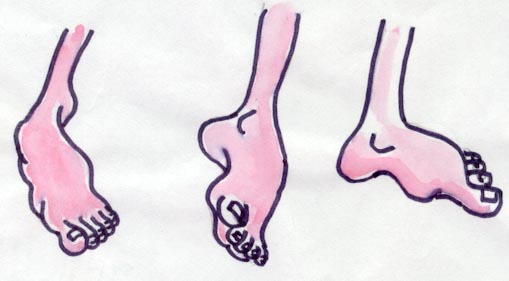 5.Deformity
of the feet
5.Deformity
of the feet
Identifying Deformities.
FLAT FOOT 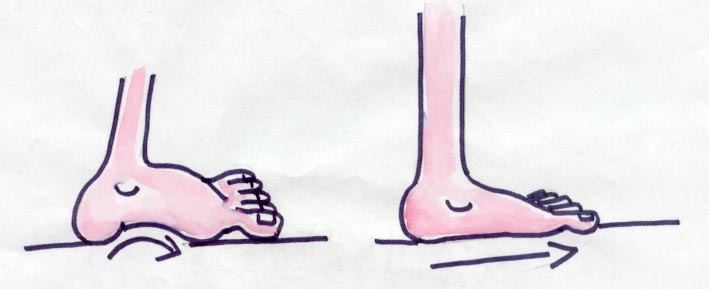
Make the patient
stand with bare feet; with legs a
little apart.
Look for any arch on the inner side of both feet. If the central
portion of the of the inner border of the feet touch the floor, it indicates
flat feet.
CROOKED FOOT/CLUB
FOOT 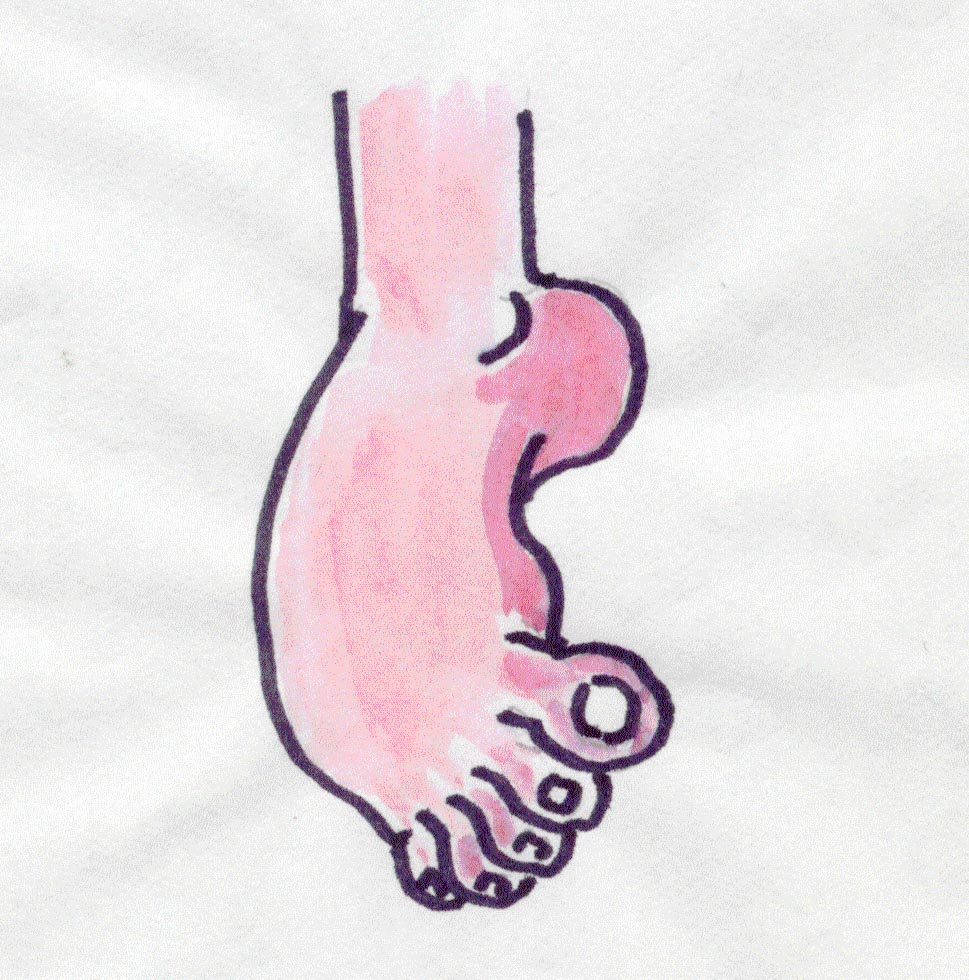
Make the child lie
on his back, with bare legs.
If one or both feet
are twisted inwards, the feet
are deformed.
Remedial Measures
1. Refer the patient
to the Rehabilitation unit of
the
Primary Health Centre.
2. If an assistive
device can correct the deformity,
the
patient will be given the device. He must use
it regularly
for good results.
3. If exercises are
advised, the patient must learn
and
practise them regularly.
4. The patient must
examined every three months to
arrest
any further deterioration
5. If exercises/devices
do not help,the patient may be
referred
for surgery.
Exercise is essential for any child with locomotor disability whether caused by congenital deformity , polio, paralysis, cerebral palsy,stroke or amputation. Click on exercises to view in detail.